4. Minimum living standard (poverty)
Working group on Global Systems Accounting
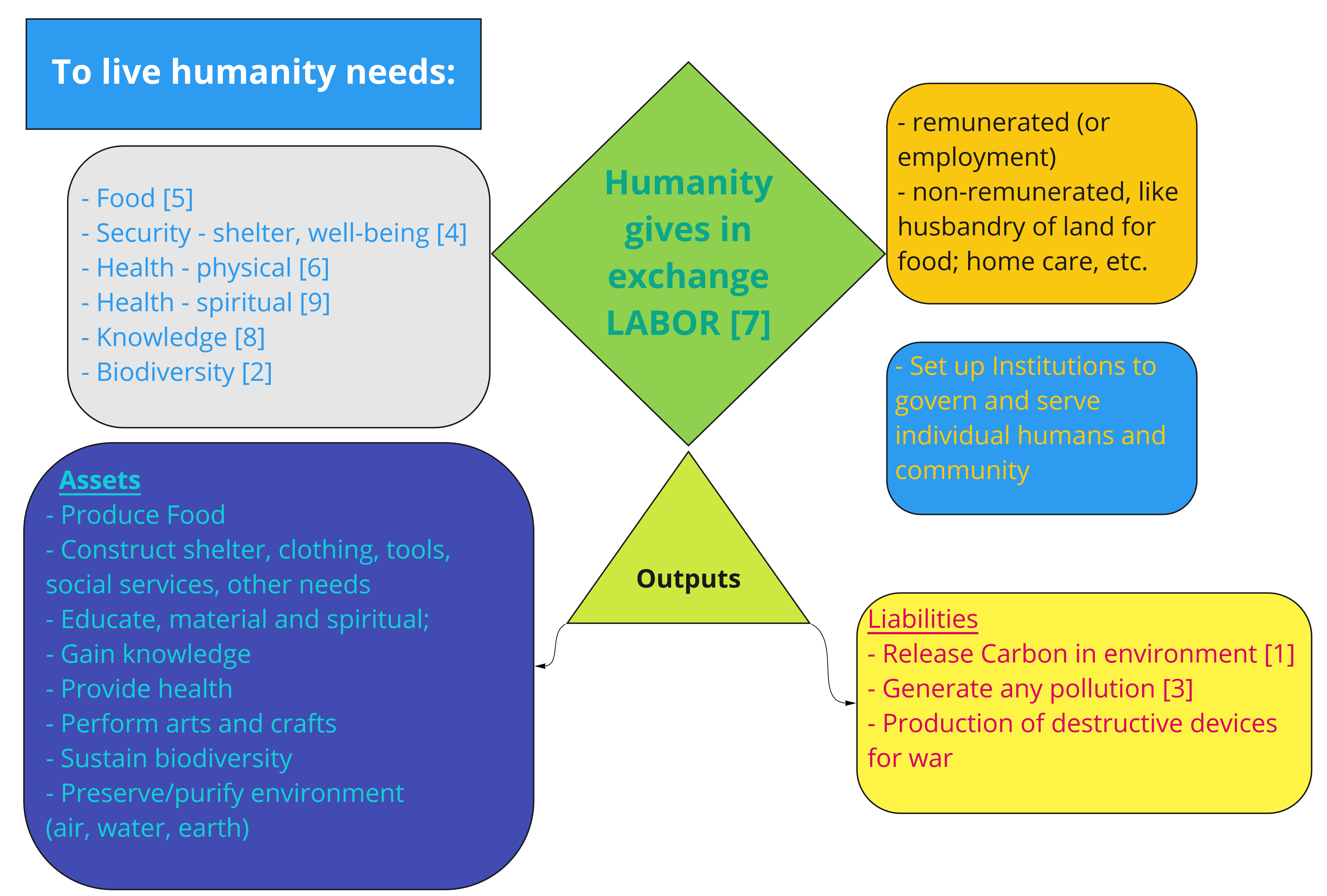
Human well-being accounting
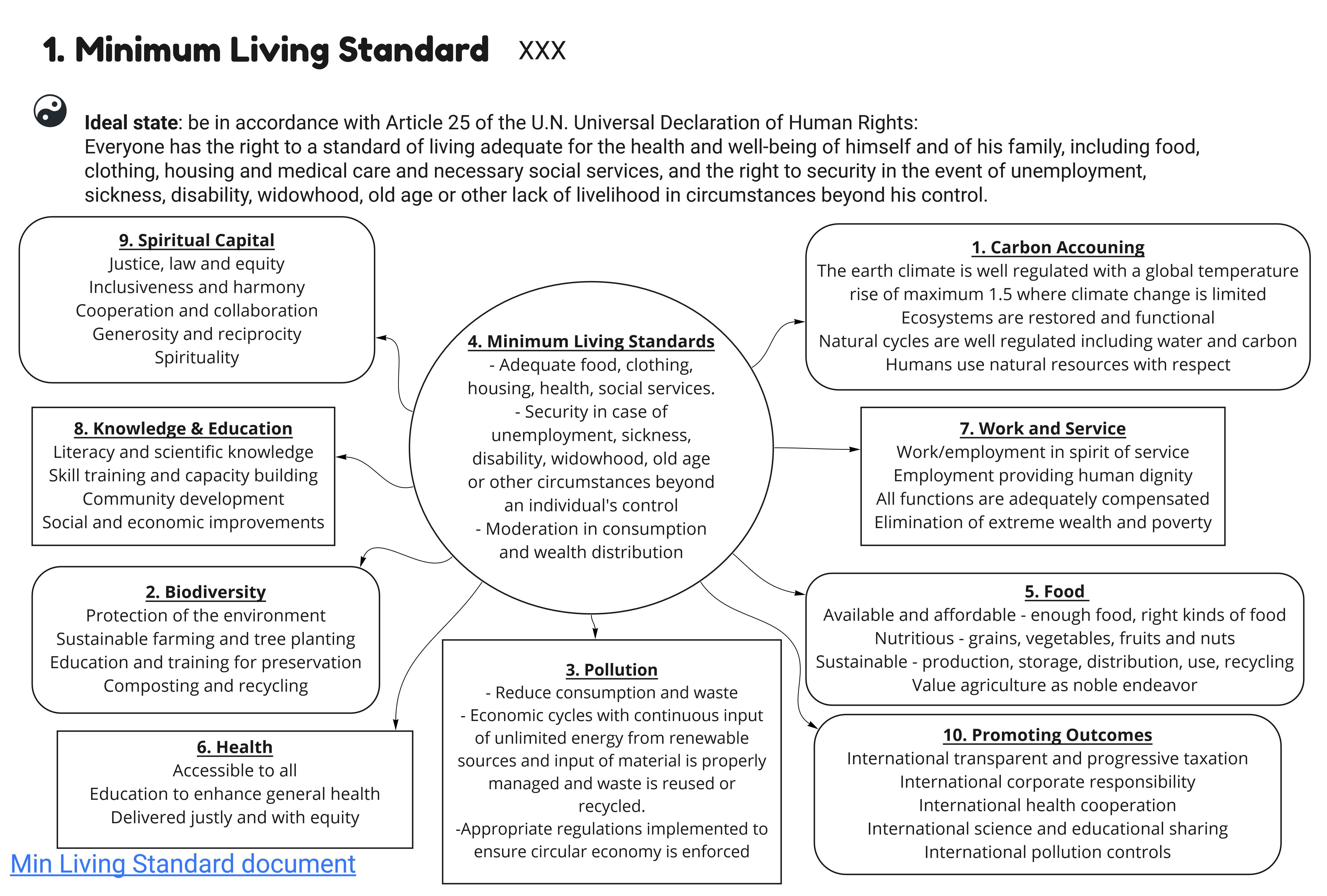
Every human being should have adequate shelter, clean water and sanitation, a source of energy and basic security as the ideal capital, with any deficiency a source of debt to be addressed.
Facilitator: Philippe Gerling
Working group members:
Description
short description
Link to the section of the background paper
Visuals/diagrams
Ideal state
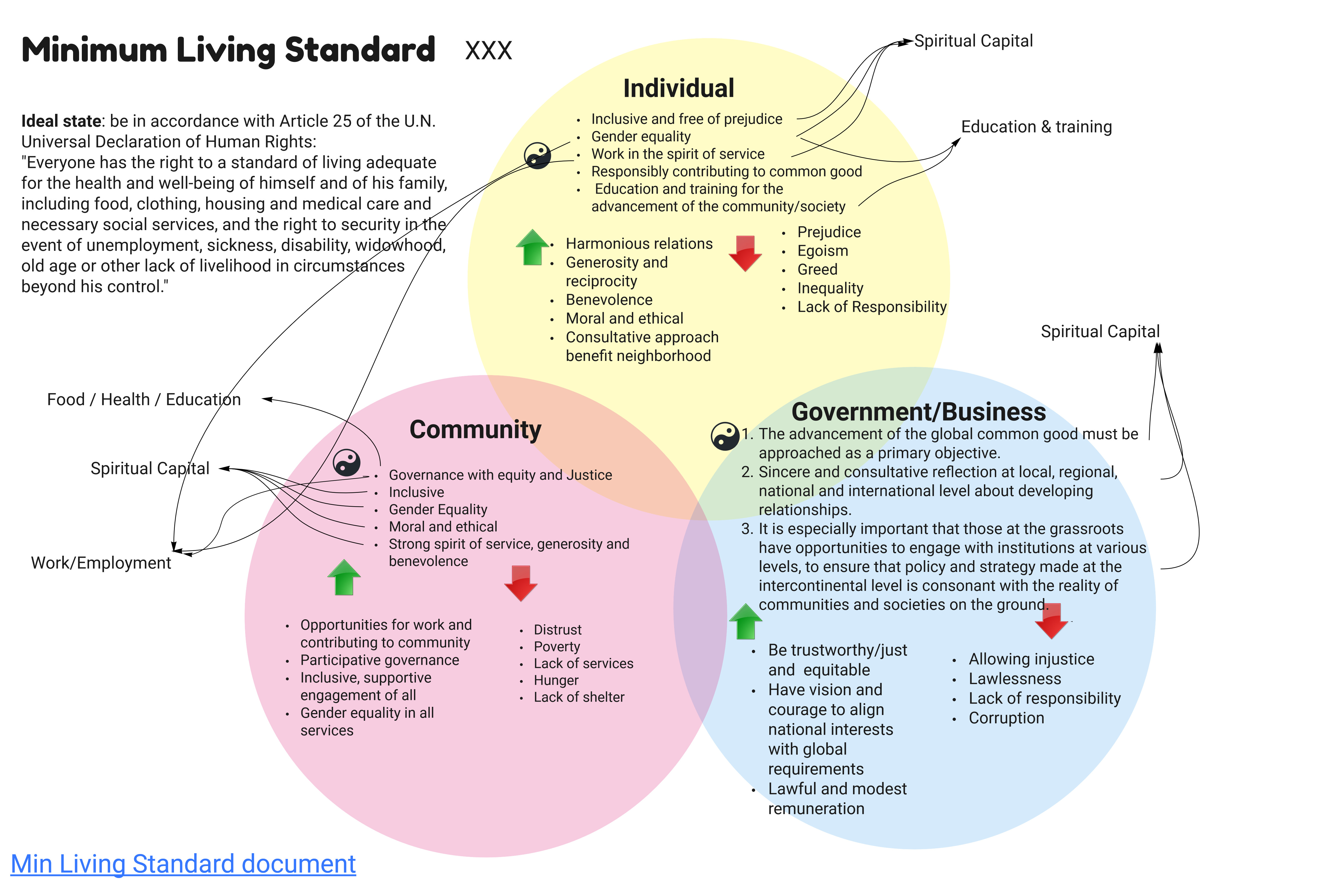
Extreme poverty in all its forms is eradicated and basic needs of all are met – (food, shelter, health, gender equality, sustainability, sustainability, climate action, peace, justice, partnerships to achieve the goal)
Non-financial currency
Nationally appropriate social protection systems and measures for all are created.
All women and men have equal rights to economic resources, access to basic services, ownership and control over land and other forms of property, inheritance, natural resources, appropriate new technology and financial services including micro-finance are operating.
Resilience of the poor and those vulnerable to climate related and extreme events and other economic, social, and environmental shocks and disasters prevention and response programs are developed and coordinated.
Sound policy-frameworks at national, regional, and international levels based on pro-poor and gender sensitive development strategies to support accelerated investment in poverty eradicating actions are developed and coordinated.
Solidarity + Generosity + Benevolence + Responsibility + Morality
Positive indicators
Basic needs are met
Potential and Opportunity are optimized for all
Justice is served
Inclusiveness + Equality + Work (rather than employment) + Education + Equity + Responsibility
National social protection systems are implemented with measured positive outcomes.
Gender equality in all sectors of social and economic life is measured with measured positive outcomes.
Programs are in place providing resilience in situations of shock/disaster on national, regional, and international levels with measured positive outcomes.
National, regional, and international frameworks are established and justly and equitably implemented and enforced to manage worldwide balanced management programs for all dimensions.
Negative indicators
Prejudice + Egoism + Greed + Inequality (is a symptom of the others) + Lack of Responsibility
Basic Needs are not supplemented by the system
No alleviation of poverty through transfer of excessive material wealth to those in need
Incomplete or unequal social protection systems causing economic migration and unequal minimum living standard.
Gender inequality creating imbalances in living standards and injustice in access to social and economic resources.
Unequal application of disaster resilience measures due to lack of coordination and implementation.
Uneven application of international frameworks to establish balanced standards for the SDGs
What needs to be done
International, regional, and national agreements are implemented equally and adhered to by all nations equally.
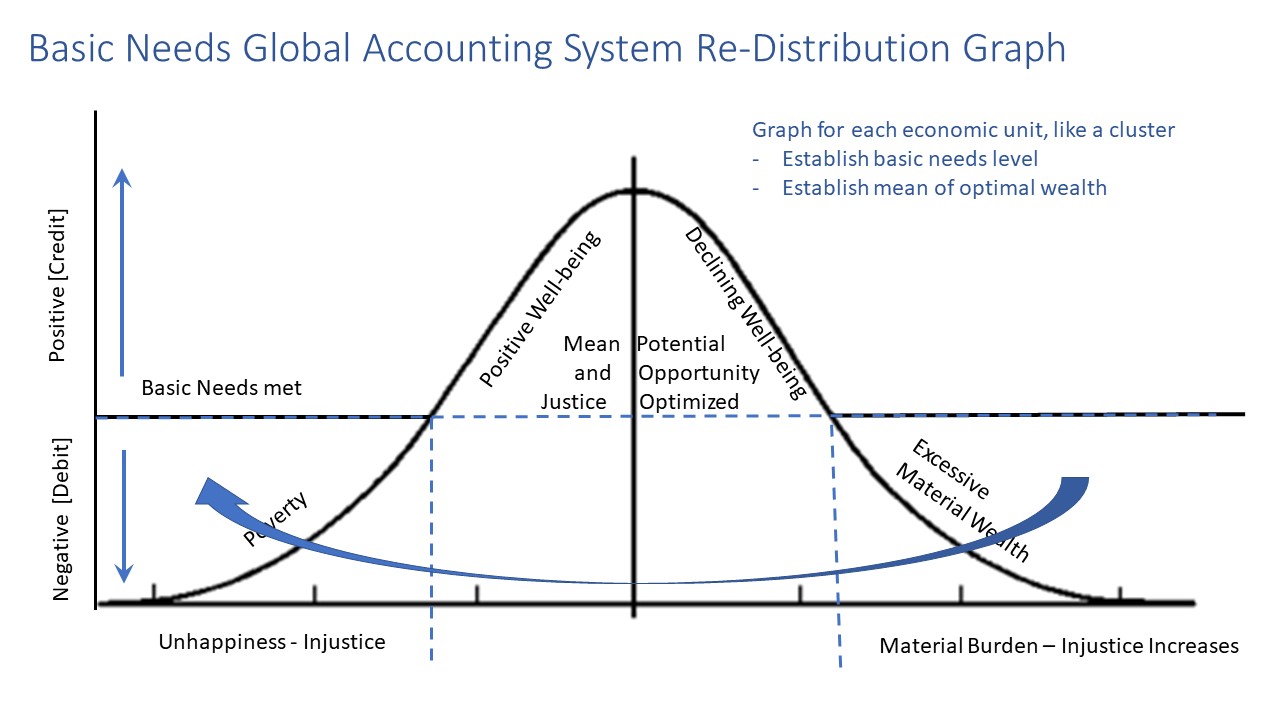
Extremes of poverty and wealth are eliminated through progressive taxation at national, regional, and international levels.
Social protection systems are supported at national, regional, and international levels.
Disaster resilience is coordinated and supported through national, regional, and international agreements.
Systems of justice and equity are implemented at national, regional, and international levels eliminating injustice, inequality and prejudicial policies and actions.
Revise disjointed and fragmented policies that alleviate poverty and obtain support for some but not all. Support should be unconditional and be considered an alienable right for all. A more transparent mechanism to move resources from those who exceed their optimal material resource (wealth) range to those who would live below the Basic Needs Line.
Example: Response to war in Ukraine – unity of nations against aggressor (economic sanctions). However, response is lacking for wars in Eritrea, Yemen, Sahel Africa and other wars. Creation of U.N. after WWII but the Security Council allows some nations to veto actions that are not in their favor. Unity has not been achieved to allow all mankind to be included and benefit from peace, security and minimum living standards.
Current state of the art
References
A New Framework for Global Prosperity https://www.bic.org/statements/new-framework-global-prosperity
Abdu’l-Bahá, The Promulgation of Universal Peace: Talks, p. 77 https://www.bahai.org/library/authoritative-texts/abdul-baha/promulgati…
Return to Global Systems Accounting page

Last updated 2 May 2022
